Table of Contents
Overview – Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
Hodgkin’s Lymphoma is a type of malignant lymphoma involving abnormal B-lymphocytes and characterised by the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells. It accounts for around 15% of all lymphomas and typically presents in young adults. Although its aetiology remains unclear, Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) is a known risk factor. With appropriate therapy, Hodgkin’s Lymphoma carries a high cure rate and favourable prognosis.
Definition
- A malignant neoplasm of B-cell lineage, affecting lymph nodes and sometimes peripheral organs
- Hallmark: Reed-Sternberg cells (large, abnormal multinucleated B-cells)
Aetiology
- Idiopathic
- EBV infection – linked to 40–50% of cases
- Risk factors:
- Family history
- Male gender
- Immunosuppression
Pathophysiology
- Malignant transformation of B-lymphocytes
- Proliferation of tumour cells within lymph nodes → painless lymphadenopathy
- Systemic spread to spleen, liver, bone marrow
- Reed-Sternberg cells secrete cytokines → systemic symptoms (“B symptoms”)
Clinical Features
Age Distribution
- Bimodal:
- Peak 1: Young adults (15–35 years)
- Peak 2: Older adults (55+ years)
Symptoms
- Painless, asymmetrical lymphadenopathy
- Commonly cervical or axillary
- B symptoms:
- Fever
- Night sweats
- Weight loss
- Pruritus
- Alcohol-induced lymph node pain (pathognomonic)
- Hepatosplenomegaly
Investigations
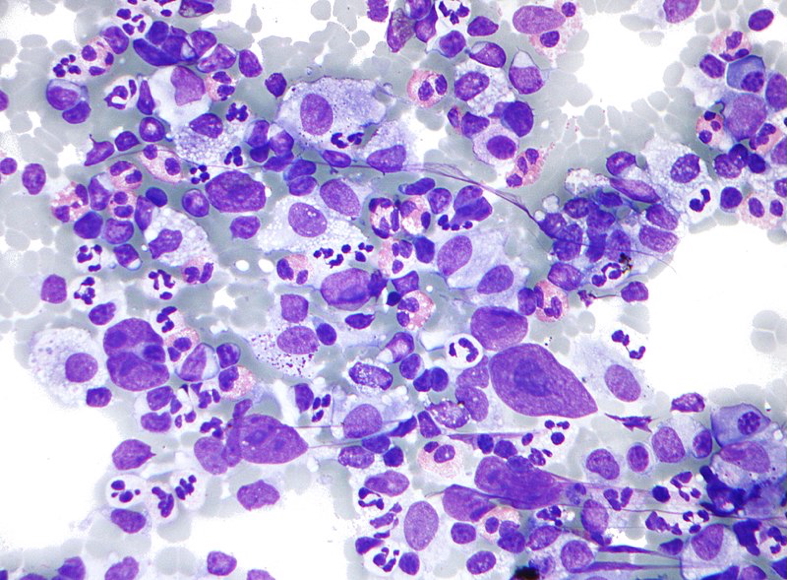
- Lymph node biopsy:
- Confirms diagnosis
- Presence of Reed-Sternberg cells (binucleated or multinucleated giant cells)
- Bone marrow biopsy (for staging)
- CT scan (chest, abdomen, pelvis):
- Evaluates extent of disease and mediastinal mass
- Blood tests:
- FBC, LDH, ESR (for inflammation and disease activity)

Management
- Depends on Ann Arbor staging
- Curative intent in most cases
- Early-stage disease:
- Radiotherapy +/- chemotherapy
- Advanced disease:
- Combination chemotherapy (e.g., ABVD regimen)
- Refractory/relapsed disease:
- Autologous stem cell transplant
Complications
- SVC obstruction:
- Due to mediastinal masses
- Presents with ↑JVP, facial swelling, and dyspnoea
- Long-term treatment complications:
- Secondary malignancies
- Infertility
- Cardiotoxicity (from anthracyclines)
Summary – Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
Hodgkin’s Lymphoma is a highly curable malignancy of B-lymphocytes, frequently presenting with painless lymphadenopathy and B symptoms in young adults. Diagnosis is confirmed by lymph node biopsy showing Reed-Sternberg cells. Treatment varies by stage and typically involves chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy. For more, see our Blood & Haematology Overview page.