Table of Contents
Overview – Lymphangitis
Lymphangitis is an acute inflammation of the lymphatic vessels, most commonly caused by bacterial infection. It is often seen in the context of soft tissue infection and may progress rapidly to cellulitis, abscess formation, or even systemic sepsis if untreated. Prompt recognition and early antibiotic therapy are essential to prevent complications and systemic involvement.
Definition
Lymphangitis refers to the inflammation of the lymphatic channels, typically resulting from bacterial invasion through a skin wound or infection.
Aetiology
- Most commonly caused by:
- β-haemolytic Streptococcus
- Staphylococcus aureus
Pathogenesis
- Bacterial inoculation (usually via skin break) → Ascending infection via lymphatic vessels
- → Acute inflammatory response along the lymphatics
- If severe:
- → Cellulitis
- → Abscess formation
- → Bacteraemia or sepsis (in advanced cases)
Clinical Features
- Systemic symptoms:
- Fever
- Chills
- Malaise
- Local signs:
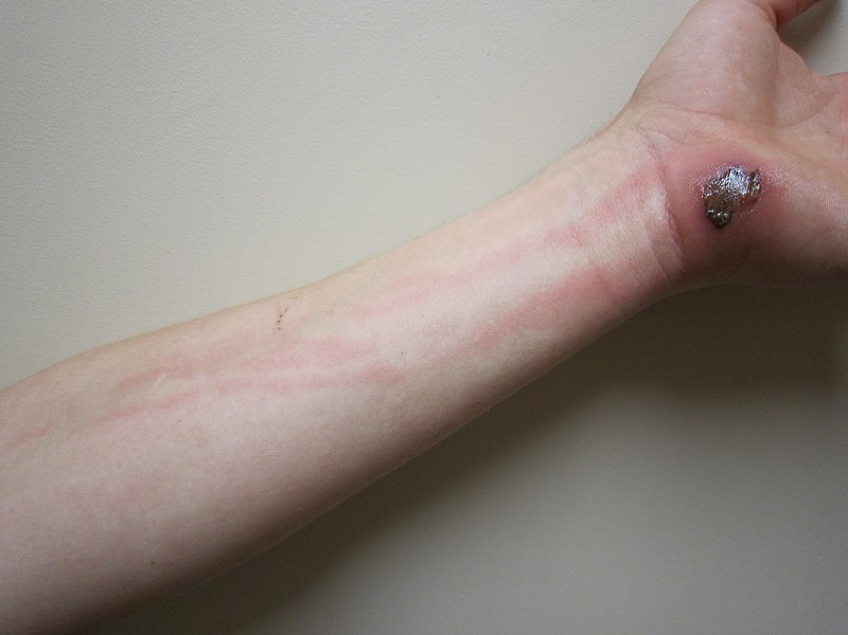
- Painful red streaks extending from infected area towards regional lymph nodes
- Tender lymphadenitis (enlarged, painful draining lymph nodes)
- Local swelling and erythema
Investigations
- Blood cultures – particularly if febrile or signs of systemic infection
- Swab cultures – of any open wound or skin break
- Full blood count (FBC) – leukocytosis
- C-reactive protein (CRP) – may be elevated in systemic inflammation
Management
- Immobilisation of the affected limb to reduce spread
- Empirical antibiotics – adjusted based on culture results
- Typically cover Streptococcus and Staphylococcus
- Analgesia for pain management
- Hospital admission if signs of sepsis or failed outpatient treatment
Complications
- Cellulitis
- Abscesses
- Sepsis
- Requires urgent intervention to prevent multi-organ failure
Summary – Lymphangitis
Lymphangitis is an acute bacterial infection of the lymphatic vessels, usually caused by β-haemolytic Streptococcus or Staphylococcus aureus. It presents with red streaks, tender lymph nodes, fever, and systemic symptoms. Complications include cellulitis, abscesses, and sepsis. For a broader context, see our Cardiovascular Overview page.