Table of Contents
Overview – Diabetes
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disorder characterised by elevated blood glucose levels (hyperglycaemia) due to impaired insulin secretion, insulin action, or both. It is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide due to its acute metabolic derangements and long-term microvascular and macrovascular complications. This article covers the physiology of insulin and glucagon, types of diabetes, diagnostic criteria, presentations, treatment options, and complications.
Physiology of Insulin & Glucagon
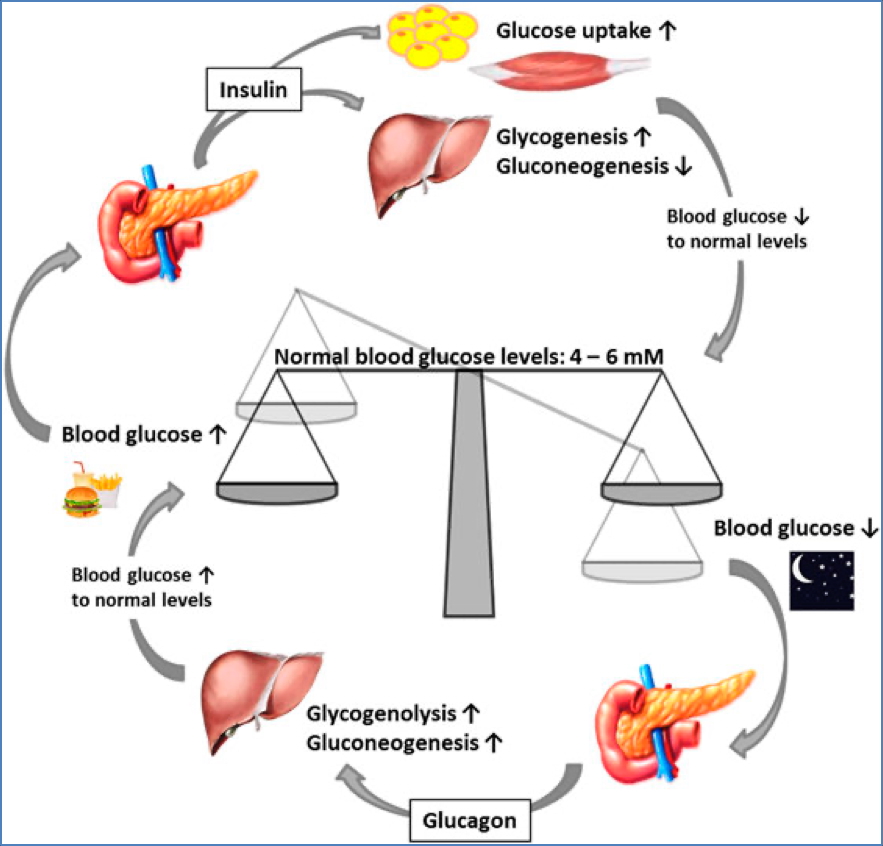
Insulin
Released in response to:
- ↑ Blood glucose
- ↑ Blood amino acids
Stimulates:
- Glucose uptake (muscle, adipose)
- Lipid synthesis/storage
- Protein synthesis
Inhibits:
- Ketogenesis
- Macromolecular breakdown
Glucagon
Released in response to:
- ↓ Blood glucose
- ↓ Blood amino acids (e.g. fasting)
Stimulates:
- Glycogenolysis
- Gluconeogenesis
- Lipolysis
- Ketogenesis
Inhibits:
- Storage/synthesis of macromolecules
Diagnostic Criteria (The “7–11 Rule”)
- Fasting BSL ≥ 7.0 mmol/L
- Random BSL > 11.1 mmol/L
- OGTT (2hr post-load) > 11.1 mmol/L
- HbA1c used for monitoring, not diagnosis
- Type 1 diabetes:
- Anti-GAD, Anti-Islet Cell Antibodies
Types of Diabetes
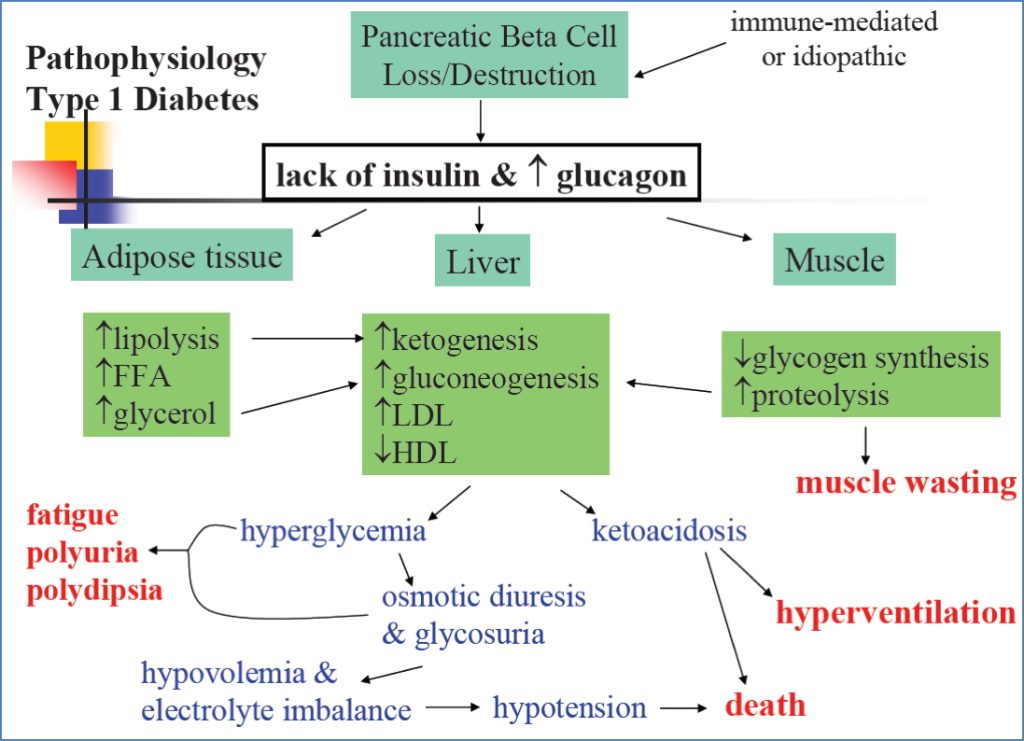
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
- Aetiology: Autoimmune β-cell destruction
- Onset: Juvenile, rapid
- Diagnosis: + Anti-GAD, Anti-ICA, Insulin Autoantibodies
- Clinical Features:
- Polyuria, polydipsia, weight loss
- Ketonuria → DKA risk
- Treatment: Exogenous insulin
- Complications: DKA
LADA (Latent Autoimmune Diabetes of Adults)
- Aetiology: Delayed-onset autoimmune
- Presentation: Slim adults, positive autoantibodies
- Complications: DKA, HONK
- Treatment: Insulin
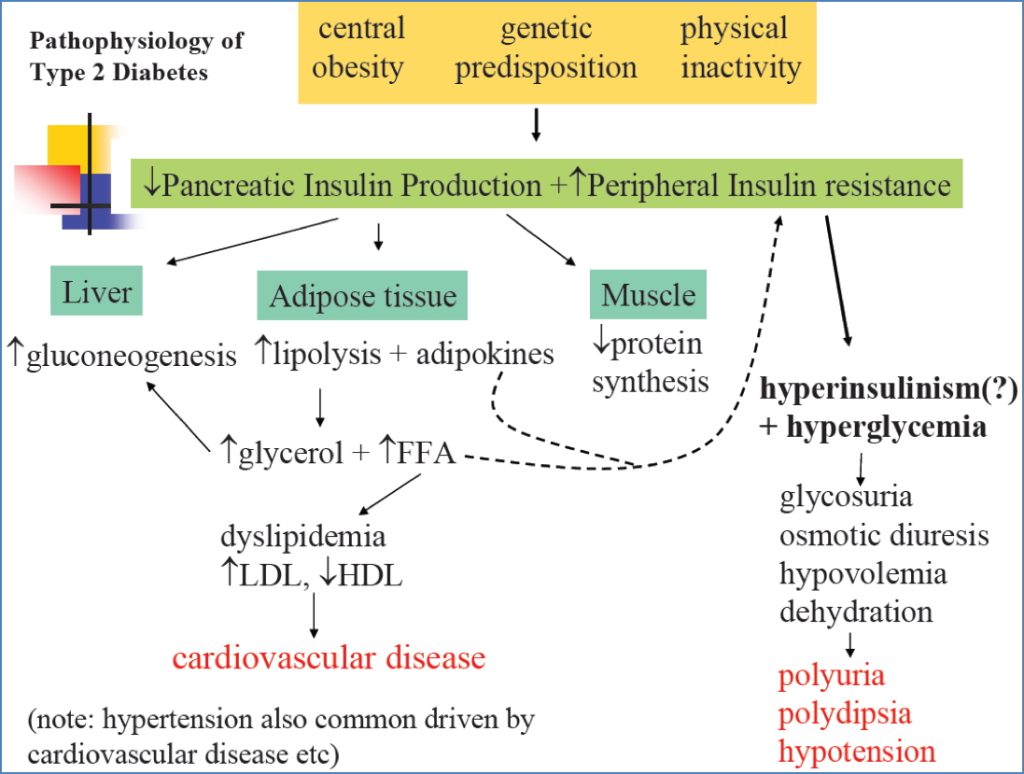
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Aetiology: Insulin resistance ± β-cell dysfunction
- Onset: Adults, insidious
- Risk Factor: Obesity (especially central)
- Metabolic Syndrome:
- ↑FFA, glucose, insulin, BP
- ↓HDL
- Diagnosis: OGTT >11 mmol/L, random BSL >11
- Treatment:
- Lifestyle
- Oral agents (Metformin, Sulfonylureas, Incretins)
- Insulin
- Complications: HONK, macro/microvascular
MODY (Maturity Onset Diabetes of the Young)
- Aetiology: Monogenic (Autosomal Dominant)
- Clinical Features: Young, non-obese, strong family history
- Treatment: Oral hypoglycaemics → insulin
Initial & Emergency Presentation
- Classic symptoms: PPP (Polyuria, Polydipsia, Polyphagia)
- Weight loss, fatigue, recurrent infections
- Emergency presentations:
- DKA (Type 1)
- HONK (Type 2)
- Hypoglycaemia
Acute Complications
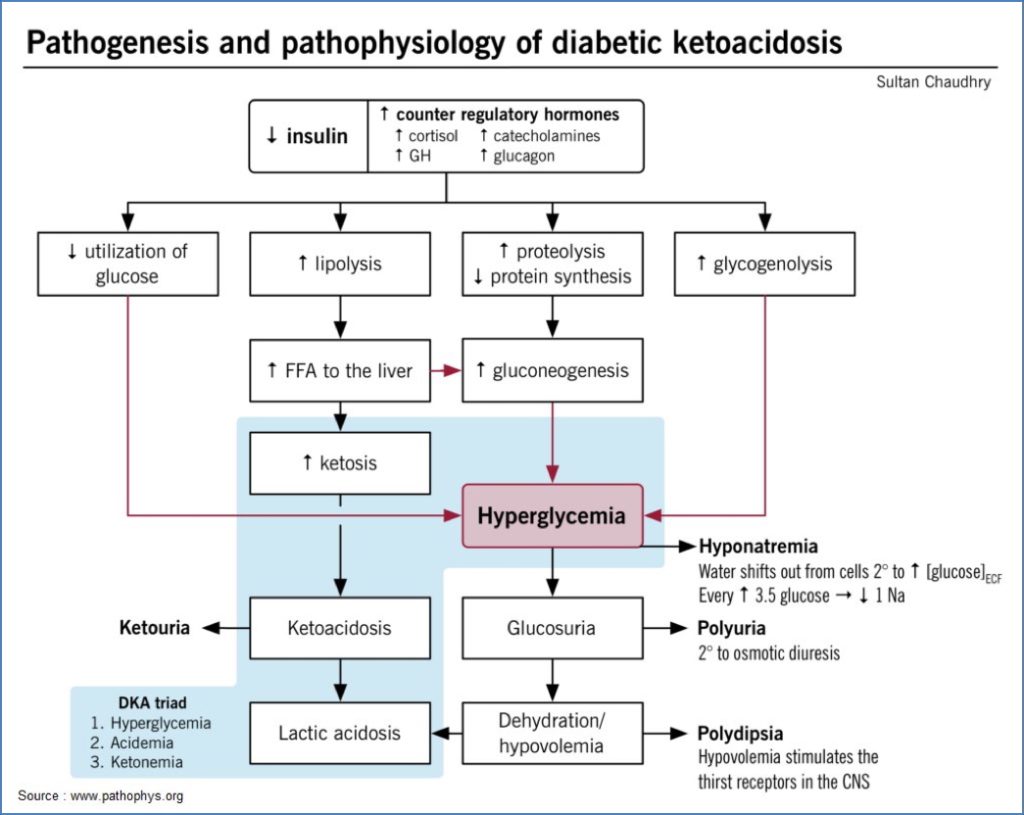
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)
- Cause: Insulin deficiency (often missed dose)
- Triad:
- Hyperglycaemia
- Metabolic acidosis
- Ketonuria
- Symptoms: Vomiting, Kussmaul breathing, acetone breath
- Treatment: IV fluids, insulin, monitor K+
- Complications: Severe dehydration, arrhythmias
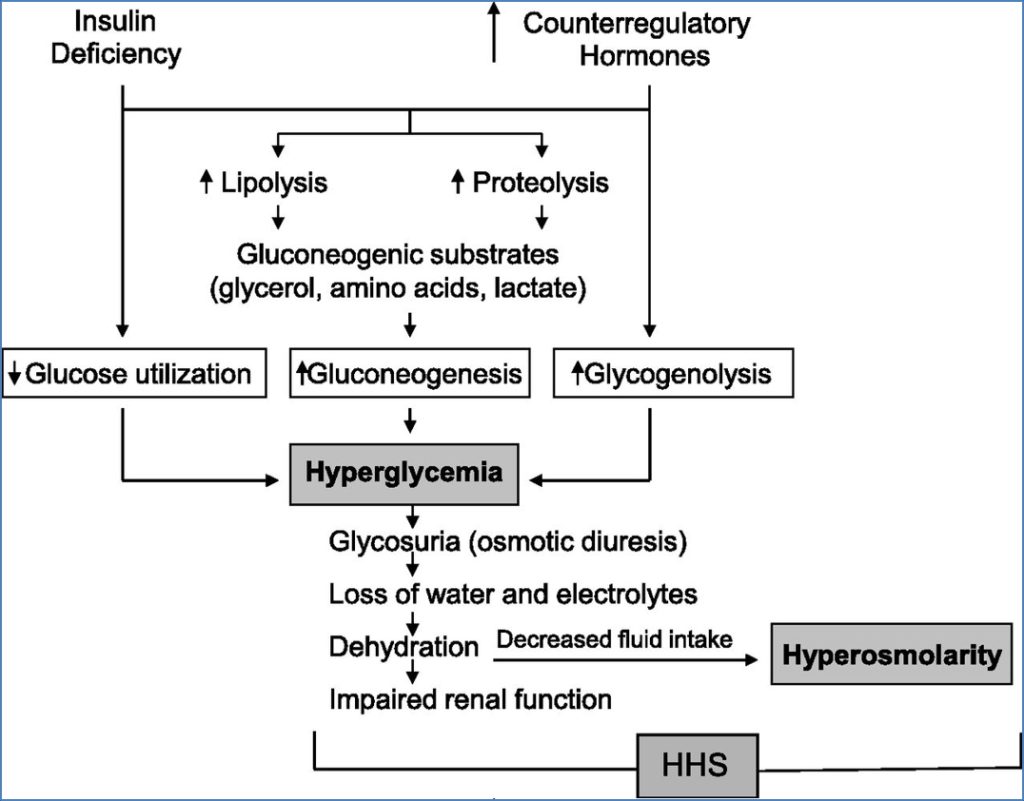
Hyperosmolar Non-Ketotic Coma (HONC)
- Cause: Type 2 DM + stressor
- Features:
- Very high BSL
- No ketosis
- Dehydration, confusion
- Treatment: IV fluids, insulin, electrolyte replacement
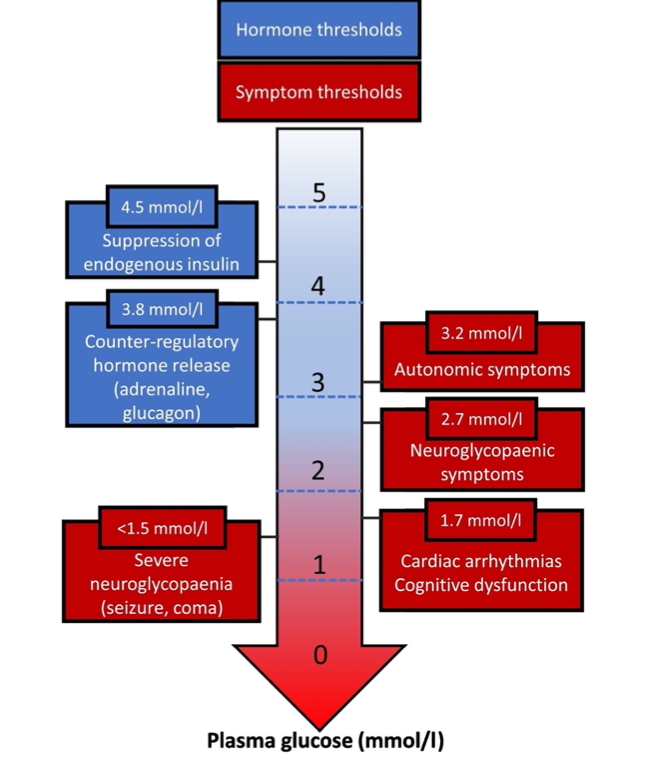
Hypoglycaemia
- BSL < 3.5 mmol/L
- Symptoms:
- Adrenergic: Sweating, tremor, palpitations
- Neuroglycopenic: Confusion, seizures, coma
- Treatment: Oral/IV glucose or IM glucagon
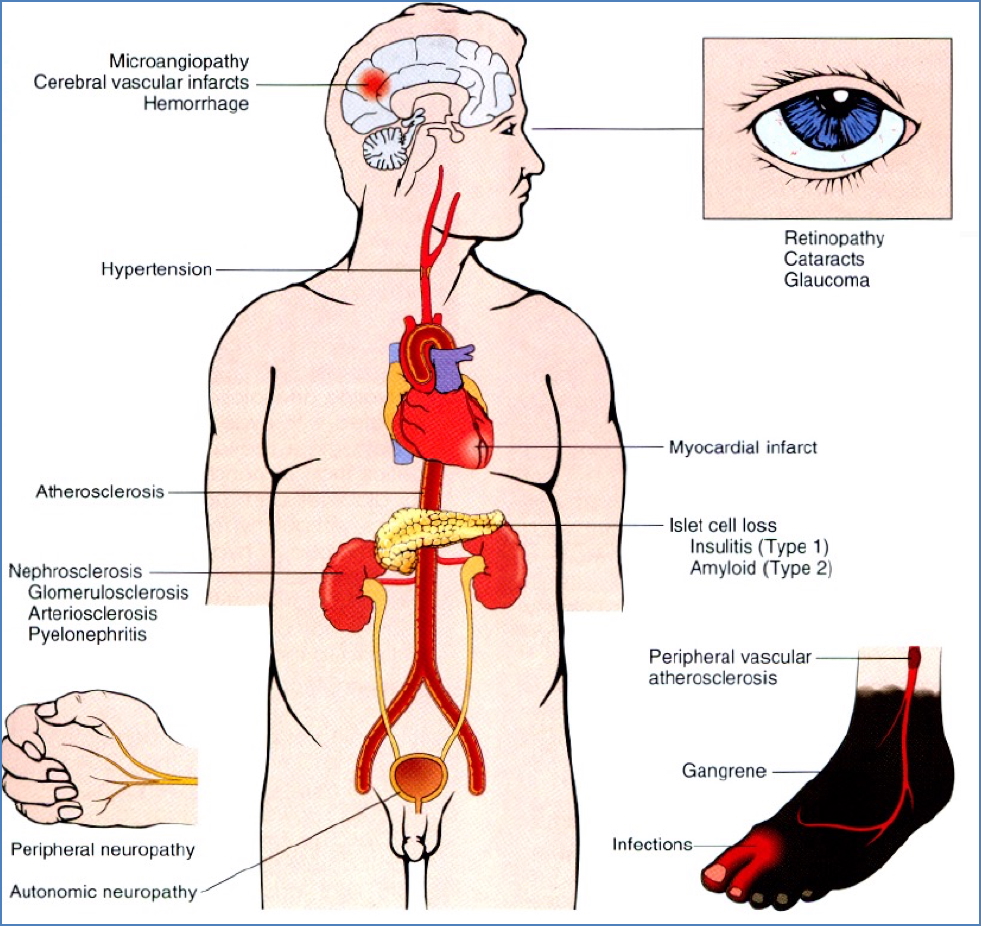
Chronic Complications
Microvascular
- Retinopathy → blindness
- Nephropathy → ESRD
- Neuropathy → foot ulcers, Charcot joints
Macrovascular
- MI
- Stroke
- Peripheral vascular disease
Pathogenic Mechanisms
Polyol Pathway
- Glucose → sorbitol → fructose
- Sorbitol accumulation → osmotic stress

Advanced Glycation End-products (AGEs)
- Non-enzymatic glycation of proteins → vessel damage
- ↓NO availability → impaired vasodilation
- ↑Matrix deposition, inflammation
Oxidative Stress
- Hyperglycaemia → ↑ROS
- Promotes endothelial dysfunction
Summary – Diabetes
Diabetes mellitus encompasses a group of metabolic diseases defined by chronic hyperglycaemia due to insulin deficiency, resistance, or both. It manifests acutely as DKA or HONK and has long-term complications affecting vascular, renal, and nervous systems. Timely diagnosis, lifestyle management, and glycaemic control are crucial. For more, visit our Endocrine Overview page.