Table of Contents
Overview – Endocrine Pancreas
The endocrine pancreas plays a central role in glucose homeostasis through tightly regulated secretion of insulin, glucagon, and other hormones. Located within the islets of Langerhans, these hormones regulate carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism across both the fed and fasted states. Understanding the endocrine pancreas is crucial for diagnosing and managing metabolic conditions like diabetes mellitus.
General
- The pancreas is an elongated, retroperitoneal organ with both exocrine and endocrine functions.
- The endocrine component constitutes about 1% of total pancreatic cells, located in the islets of Langerhans.
- The remaining 99% consists of exocrine acinar cells producing digestive enzymes.
Anatomy
Gross Structure
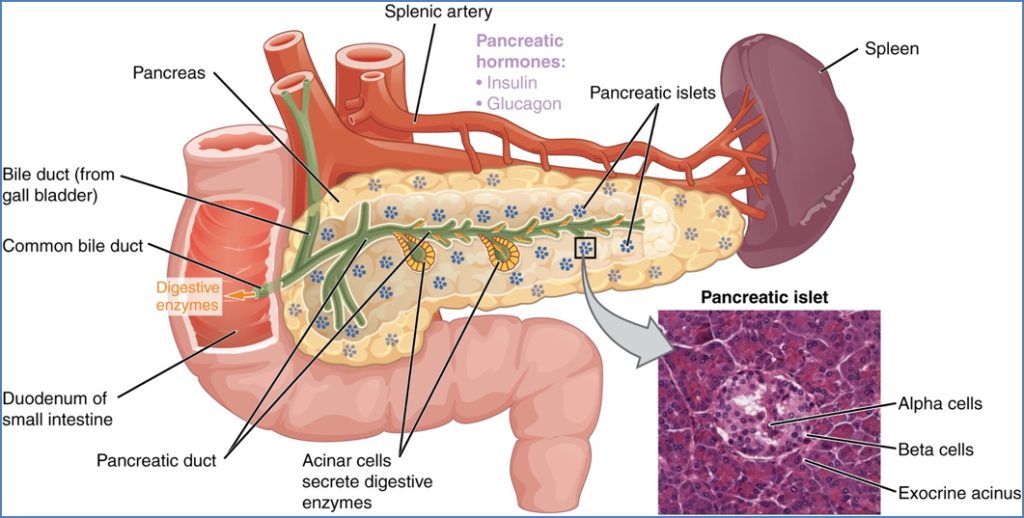
Cellular Composition of Islets
- Alpha (α) cells (25%) – Secrete glucagon.
- Beta (β) cells (60%) – Secrete insulin.
- Delta (δ) cells (10%) – Secrete somatostatin.
- PP cells (5%) – Secrete pancreatic polypeptide.
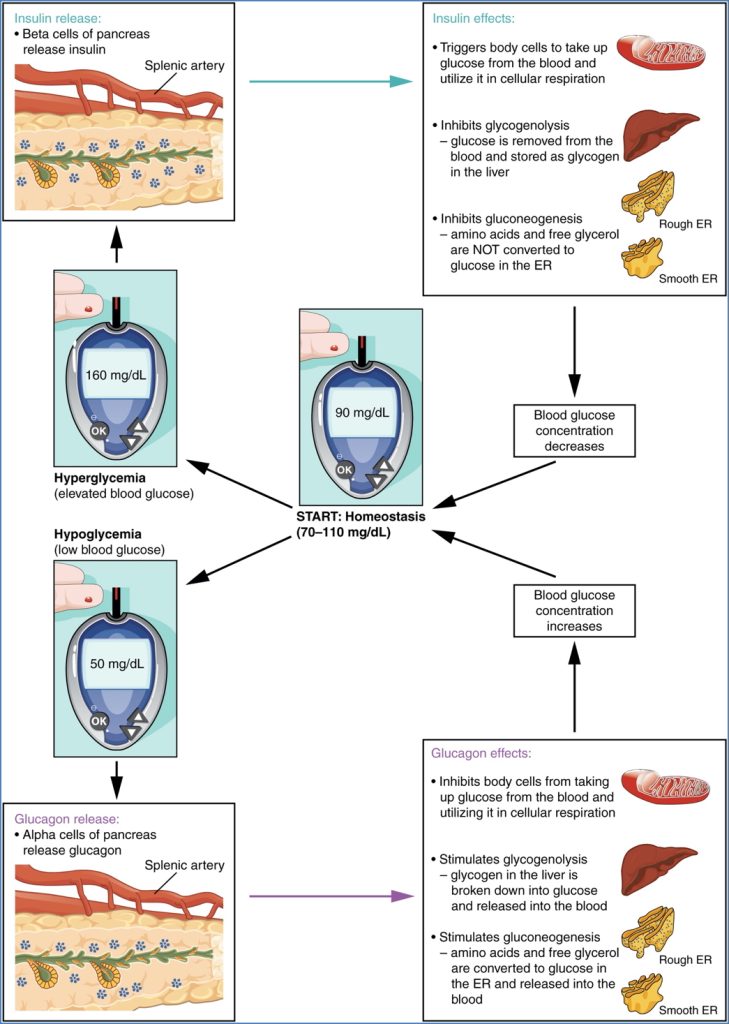
Pancreatic Hormones
Insulin
Secreted by
- Beta cells.
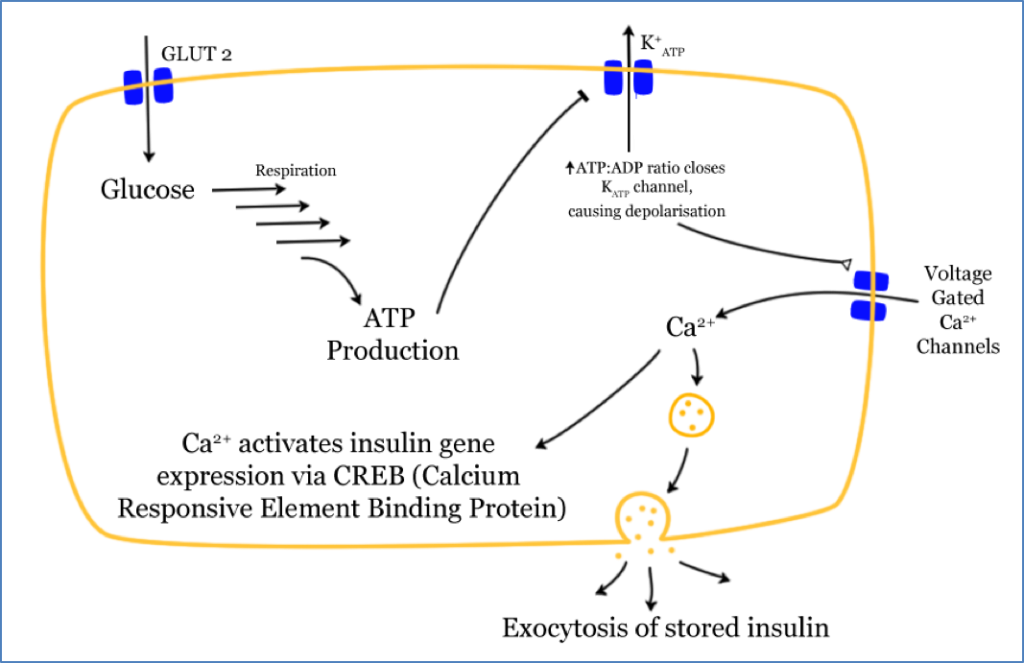
Mechanism of Secretion
- ↑ Blood glucose → glucose enters β-cells via GLUT-2.
- ↑ ATP production closes ATP-gated K+ channels.
- Membrane depolarization opens voltage-gated Ca²⁺ channels.
- Ca²⁺ influx triggers exocytosis of insulin granules.
Insulin-Sensitive Tissues
- Liver, muscle, adipose (express GLUT-4 transporters).
Insulin-Insensitive Tissues
- Endothelium, myocardium, nervous system, RBCs, kidneys, eyes.
Actions
- Increases GLUT-4 expression → ↑ glucose uptake.
- Stimulates:
- Glycolysis.
- Glycogenesis (liver, muscle).
- Lipogenesis (liver, adipose).
- Protein synthesis.
- Inhibits:
- Gluconeogenesis.
- Ketogenesis.
- Lipolysis, glycogenolysis, proteolysis.

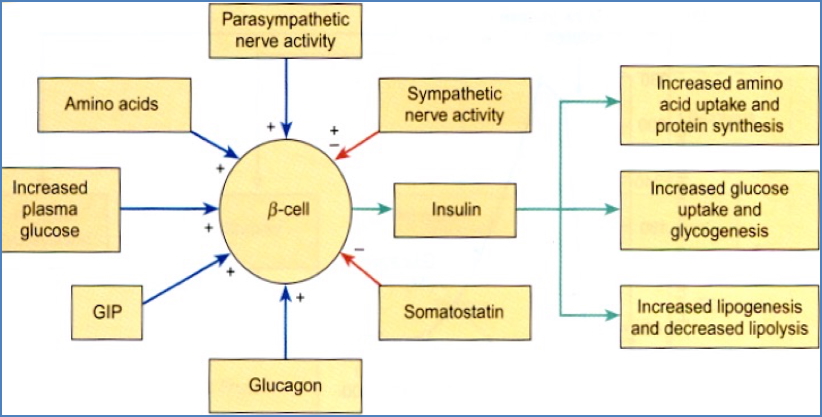
Stimulated by
- Parasympathetic NS.
- Elevated glucose and amino acids.
- Gastrointestinal peptide hormones (GIP).
- Glucagon (weak stimulator).
Inhibited by
- Sympathetic NS (stress response).
- Somatostatin.
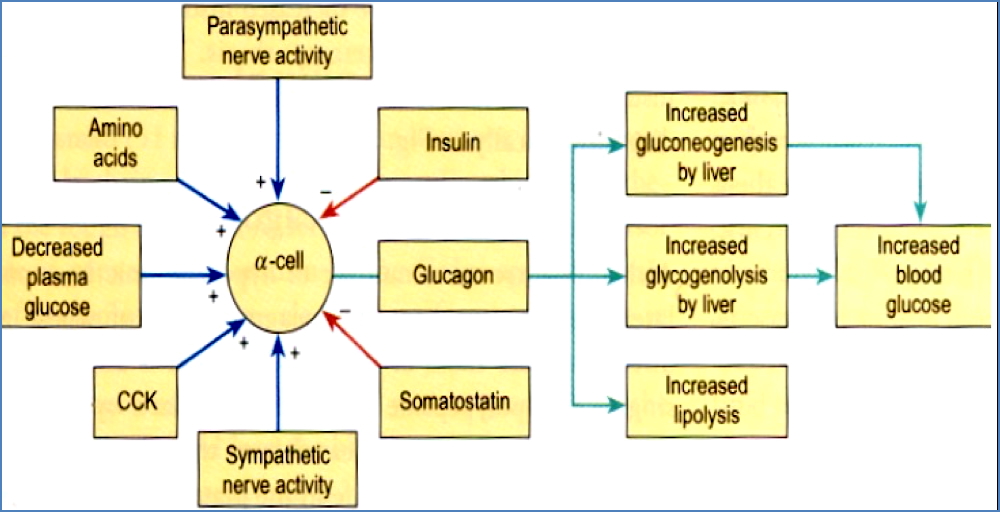
Glucagon
Secreted by
- Alpha cells.
Actions
- Increases blood glucose by:
- Glycogenolysis (liver).
- Gluconeogenesis (liver).
- Lipolysis (adipose).
- Ketogenesis (liver).
- Inhibits glycolysis, fatty acid synthesis, and fat deposition.

Stimulated by
- Hypoglycemia.
- Low insulin.
- Sympathetic drive (α-adrenergic).
- Cholecystokinin (CCK).
- Exercise.
Inhibited by
- Hyperglycemia.
- Elevated insulin.
- Parasympathetic drive (M3 receptors).
- Amino acids (alanine, arginine).
- Somatostatin.
Metabolic States
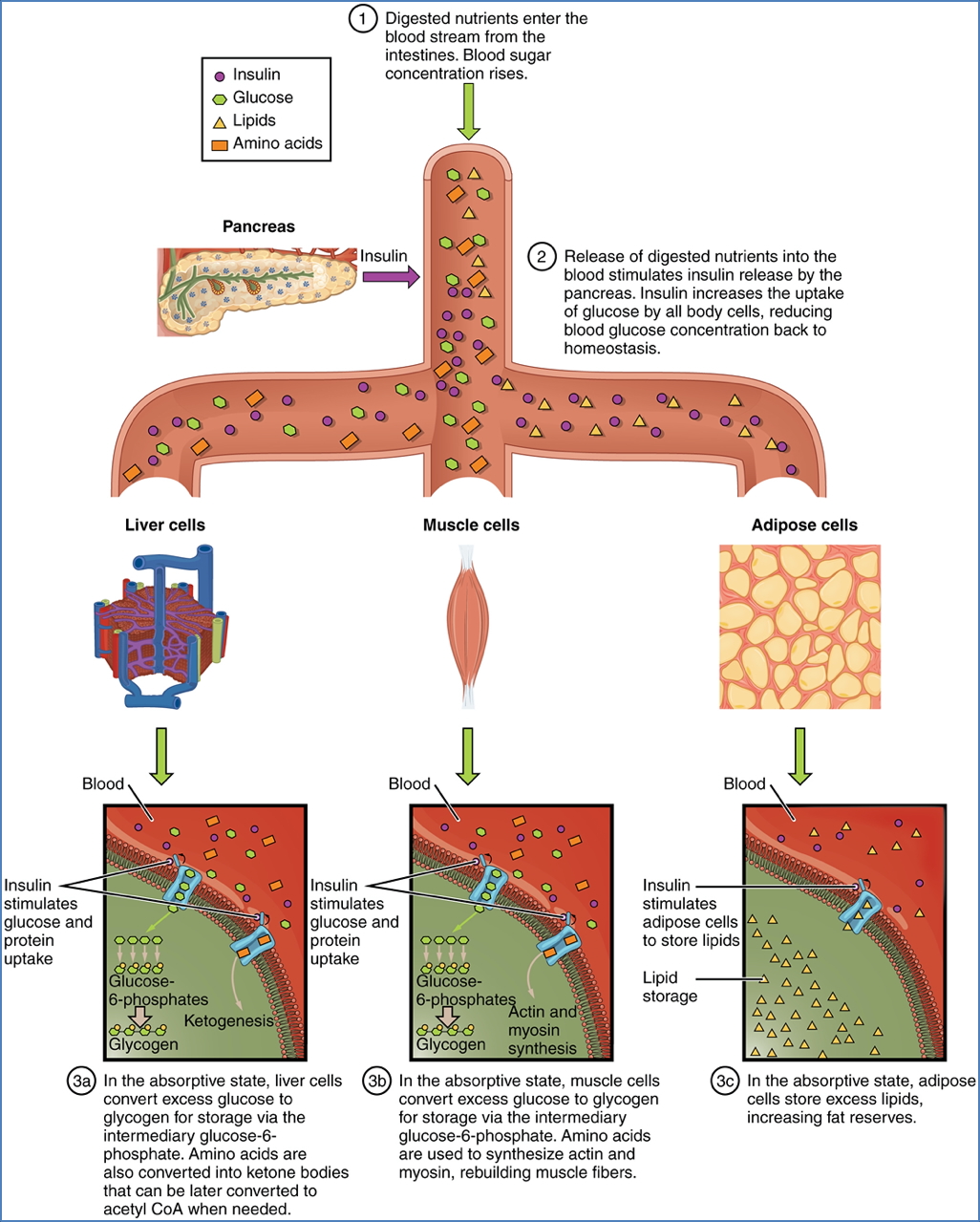
Fed State (Postprandial)
- ↑ Insulin:
- Nutrient uptake: glucose, amino acids, fatty acids.
- Promotes storage: glycogenesis, lipogenesis, protein synthesis.
- Inhibits catabolic pathways: gluconeogenesis, ketogenesis, lipolysis, glycogenolysis, proteolysis.
Incretin Effect
- Gut-derived incretins (GLP-1, GIP) further enhance insulin secretion.
- Incretins degraded by DPP-4 → pharmacologic DPP-4 inhibitors prolong incretin action.

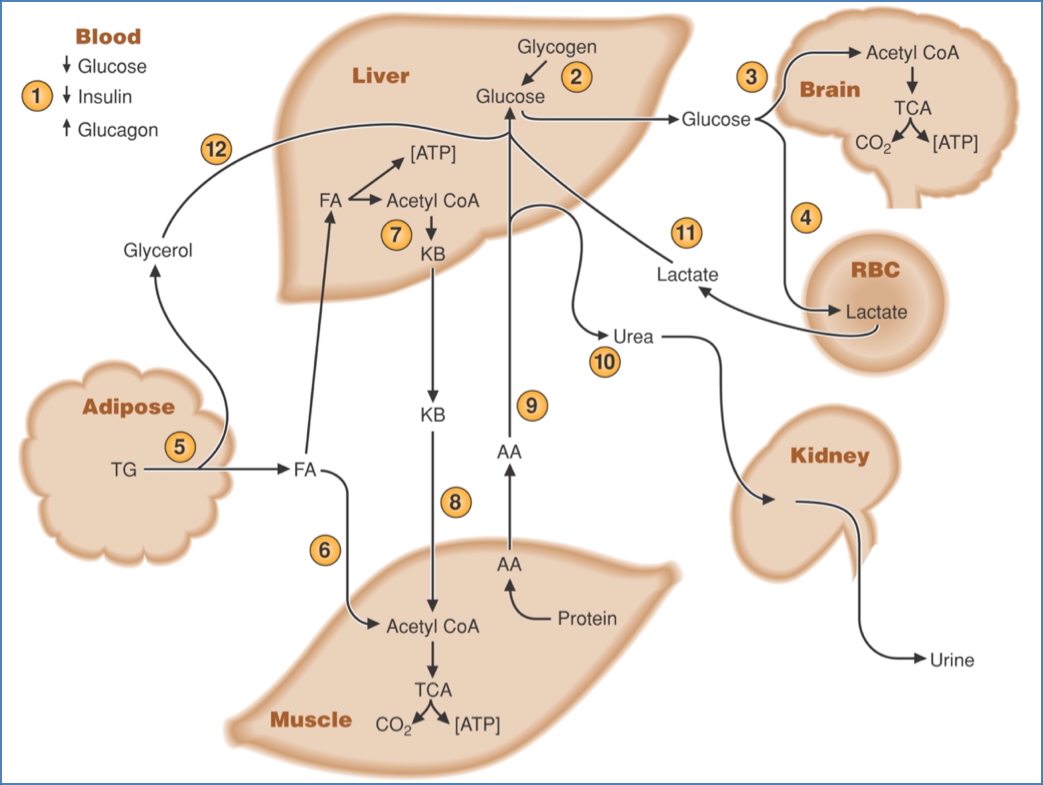
Fasted State (≈3 hours post-meal)
- ↑ Glucagon:
- Glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis maintain plasma glucose.
- Lipolysis and ketogenesis supply alternate energy substrates.
- Protein breakdown provides gluconeogenic substrates.
- ↓ Insulin permits:
- Glucose-sparing (more glucose reserved for brain and nerves).
- Limited lipolysis and ketogenesis (prevents ketoacidosis due to minimal residual insulin).

Summary – Endocrine Pancreas
The endocrine pancreas, via its specialized islet cells, tightly regulates blood glucose through insulin and glucagon secretion, coordinating complex metabolic pathways in both the fed and fasted states. This balance is essential for metabolic homeostasis and is frequently disrupted in disorders such as diabetes. For a broader context, see our Endocrine Overview page.