Table of Contents
Overview – Gout
Gout, or gouty arthritis, is a metabolic inflammatory arthritis caused by hyperuricaemia and the deposition of monosodium urate crystals in joints and soft tissues. It commonly presents as sudden, intensely painful attacks of monoarthritis, often affecting the first metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint. Early diagnosis and management are essential to prevent long-term joint damage, kidney complications, and recurrent flares.
Definition
Gout is an inflammatory arthritis caused by crystal deposition of monosodium urate in joints and soft tissues due to elevated serum uric acid levels.
Aetiology
Primary Causes
- Increased uric acid production or reduced excretion
- High purine intake (e.g., red meats, seafood, alcohol)
Secondary Causes
- Renal failure (↓ excretion)
- Thiazide diuretics
- Hypothyroidism
- Haemolysis
- Obesity
Pathogenesis
- Purine metabolism disorder → Hyperuricaemia
- Crystals of monosodium urate deposit in joints
- Acute inflammation ensues
- Chronic: Formation of gouty tophi → joint destruction
Morphology
- Macro:
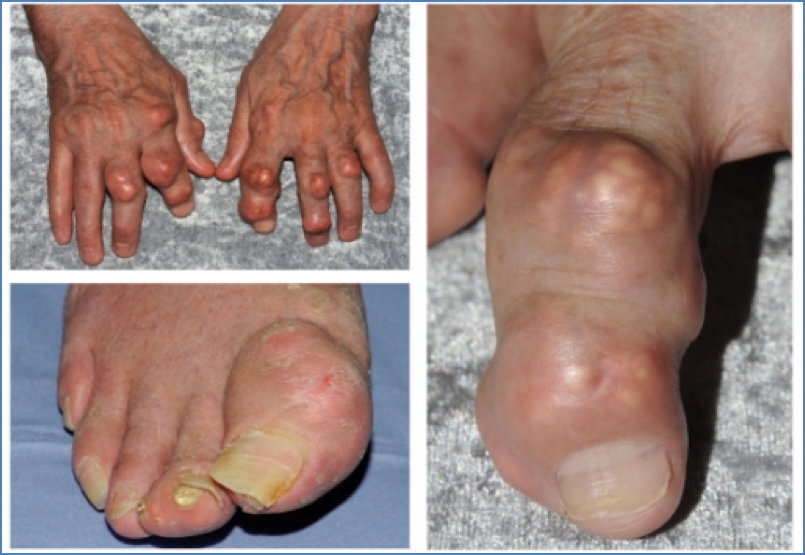
- Red, hot, swollen joints (especially the 1st MTP joint)
- Gouty tophi in joints, tendons, bursae
- Micro:
- Needle-shaped monosodium urate crystals under polarised light
Clinical Features
- Demographics:
- Typically affects men >45 years
- Presentation:
- Recurrent acute monoarthritis
- Classically affects the 1st MTP joint
- May involve hands or knees
- Severe pain, erythema, ↓ROM (often mimics cellulitis, but with restricted movement)
- Tophi:
- Chronic urate deposits in joints/tendons
- Painless, but cause reduced mobility
- Renal complications:
- Uric acid kidney stones
- Urate nephropathy
- Recurrent acute monoarthritis
Investigations
- Clinical diagnosis (often sufficient)
- Joint aspiration:
- Needle-shaped negatively birefringent urate crystals
- Serum uric acid (may be normal during acute attacks)
Management
Acute
- NSAIDs
- Colchicine
- Corticosteroids
Prophylaxis
- Allopurinol (start after acute phase resolves)
Lifestyle
- Dietary modifications:
- Avoid high-purine foods: meats, seafood, alcohol, legumes
- Weight loss and reduced alcohol intake
Summary – Gout
Gout is a crystal-induced arthritis characterised by painful monoarthritis due to hyperuricaemia and urate crystal deposition, most often affecting the first MTP joint. Diagnosis is confirmed via crystal identification on joint aspirate. Management involves acute symptom relief and long-term uric acid control. For a broader context, see our Musculoskeletal Overview page.