Table of Contents
Overview – Upper Limb Muscles
The upper limb muscles are responsible for the complex range of motion and strength required for activities such as lifting, pushing, gripping, and fine motor control. These muscles span the shoulder girdle, arm, forearm, and hand, and are grouped by location and function. Understanding these is critical for clinical assessments of injury, nerve lesions, and rehabilitation planning.
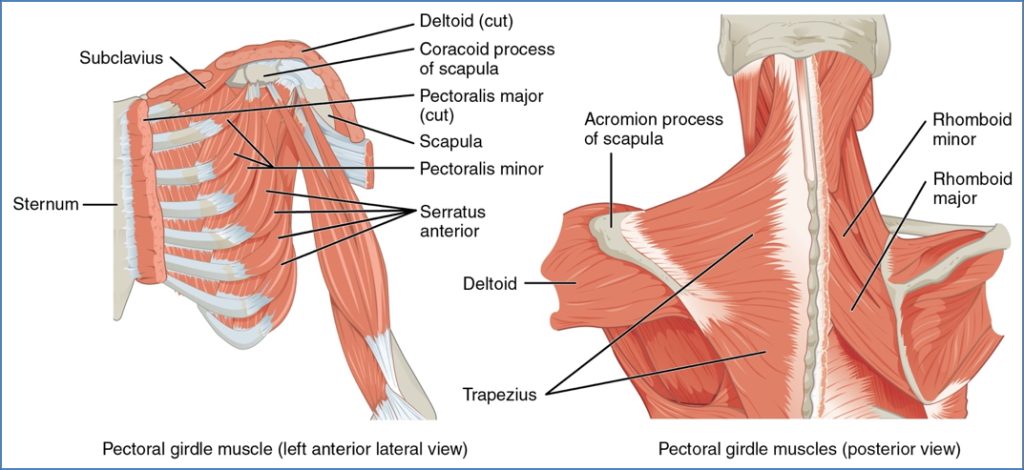
Muscles That Move the Pectoral Girdle
These muscles stabilise and position the scapula and clavicle to support upper limb function.
| Muscle | Origin / Insertion | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Trapezius | O: Occipital bone → Thoracic vertebrae I: Spine of scapula, acromion, lateral clavicle | Elevates, retracts, depresses scapula |
| Subclavius | O: Rib 1 I: Inferior clavicle groove | Stabilises & depresses pectoral girdle |
| Rhomboid Major | O: T2–T5 spines I: Lower medial border of scapula | Retracts, medially rotates scapula |
| Rhomboid Minor | O: C7–T1 spines I: Upper medial border of scapula | Retracts, medially rotates scapula |
| Levator Scapulae | O: C1–C4 transverse processes I: Medial border of scapula | Elevates & medially rotates scapula |
| Pectoralis Minor | O: Ribs 3–5 I: Coracoid process | Draws scapula forward & downward |
| Serratus Anterior | O: Ribs 1–8 I: Medial anterior scapula | Protraction of scapula; stabilises scapula |
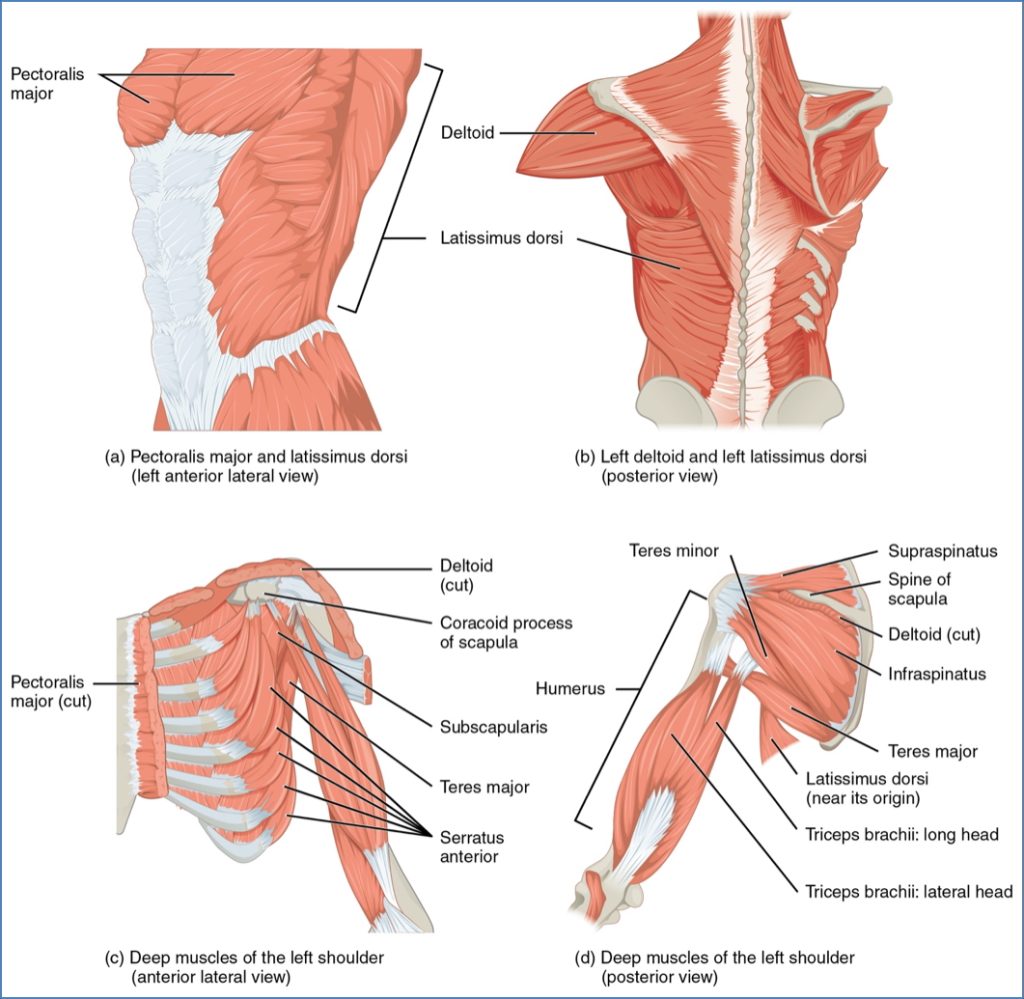
Muscles That Move the Humerus (Shoulder Joint)
These muscles control shoulder movement and stabilise the glenohumeral joint.
| Muscle | Origin / Insertion | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Supraspinatus (RC) | O: Supraspinous fossa I: Greater tubercle of humerus | Abducts humerus; stabilises joint |
| Infraspinatus (RC) | O: Infraspinous fossa I: Greater tubercle of humerus | Lateral rotation; stabilises shoulder |
| Subscapularis (RC) | O: Subscapular fossa I: Lesser tubercle | Medial rotation; joint stability |
| Teres Minor (RC) | O: Lateral scapula I: Greater tubercle | Lateral rotation; joint stability |
| Deltoid | O: Clavicle, acromion, scapular spine I: Deltoid tuberosity | Abduction, flexion, extension, rotation |
| Teres Major | O: Inferior scapula I: Intertubercular sulcus | Adduction, medial rotation |
| Latissimus Dorsi | O: Thoracolumbar fascia, ribs, pelvis I: Intertubercular sulcus | Extension, adduction, medial rotation |
| Pectoralis Major | O: Clavicle, sternum, ribs I: Greater tubercle | Flexion, adduction, medial rotation |
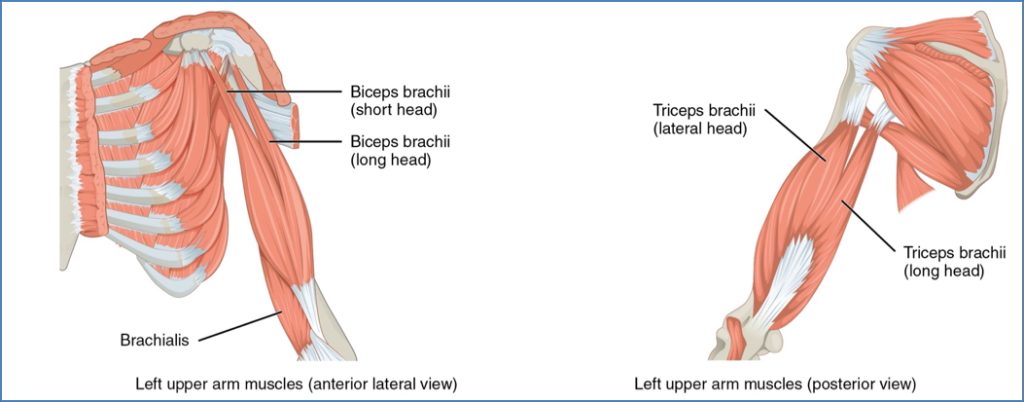
Muscles of the Arm
| Muscle | Origin / Insertion | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Biceps Brachii | O: Scapula (2 heads) I: Radial tuberosity | Elbow flexion, forearm supination |
| Brachialis | O: Anterior humerus I: Coronoid process (ulna) | Elbow flexion (main flexor) |
| Coracobrachialis | O: Coracoid process I: Medial humerus shaft | Flexion & adduction of humerus |
| Triceps Brachii | O: Scapula + posterior humerus I: Olecranon process (ulna) | Elbow extension; adduction of arm (long head) |
| Anconeus | O: Lateral epicondyle I: Olecranon (ulna) | Elbow extension, ulna abduction |
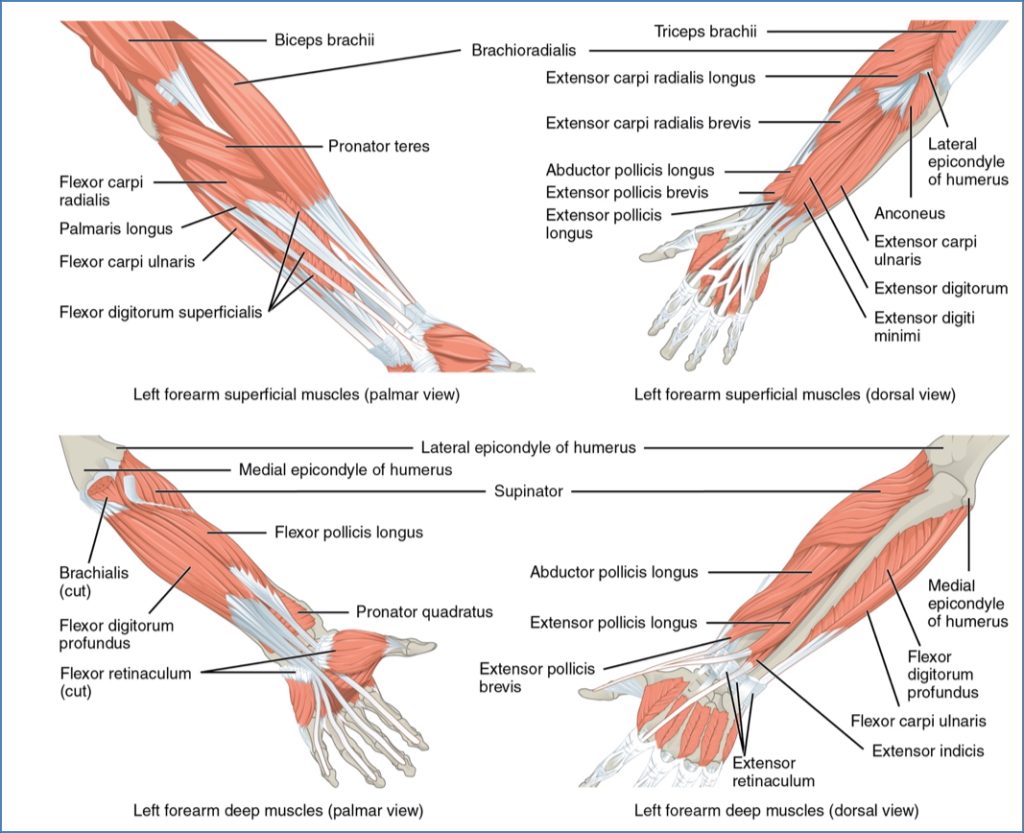
Forearm Muscles
Anterior Forearm – Superficial (Flexors)
| Muscle | Origin / Insertion | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Pronator Teres | Medial epicondyle & coronoid → radius | Forearm pronation |
| Flexor Carpi Radialis | Medial epicondyle → Metacarpals 2–3 | Wrist flexion, abduction |
| Palmaris Longus | Medial epicondyle → Palmar aponeurosis | Tenses palm, flexes wrist |
| Flexor Carpi Ulnaris | Medial epicondyle, olecranon → Pisiform, hamate, MC5 | Wrist flexion, adduction |
| Flexor Digitorum Superficialis | Medial epicondyle → Middle phalanges (2–5) | Flexion of fingers 2–5, wrist flexion |
Anterior Forearm – Deep (Flexors)
| Muscle | Origin / Insertion | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Flexor Pollicis Longus | Radius → Distal thumb phalanx | Thumb flexion |
| Flexor Digitorum Profundus | Ulna → Distal phalanges (2–5) | Flexes distal IP joints of fingers 2–5 |
| Pronator Quadratus | Distal ulna → Distal radius | Forearm pronation |
Posterior Forearm – Superficial (Extensors)
| Muscle | Origin / Insertion | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Brachioradialis | Humerus → Styloid process (radius) | Synergist in elbow flexion |
| Extensor Carpi Radialis L/B | Humerus → Metacarpals 2 & 3 | Wrist extension, abduction |
| Extensor Digitorum | Humerus → Distal phalanges (2–5) | Finger extension |
| Extensor Digiti Minimi | Humerus → Phalanx of digit 5 | Little finger extension |
| Extensor Carpi Ulnaris | Humerus → Metacarpal 5 | Wrist extension, adduction |
Posterior Forearm – Deep
| Muscle | Origin / Insertion | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Supinator | Humerus & ulna → Radius | Forearm supination |
| Abductor Pollicis Longus | Radius & ulna → MC1 & trapezium | Thumb & wrist abduction |
| Extensor Pollicis Longus | Ulna → Distal thumb phalanx | Thumb extension |
| Extensor Pollicis Brevis | Radius → Proximal thumb phalanx | Thumb extension |
| Extensor Indicis | Ulna → Extensor expansion of digit 2 | Index finger extension |

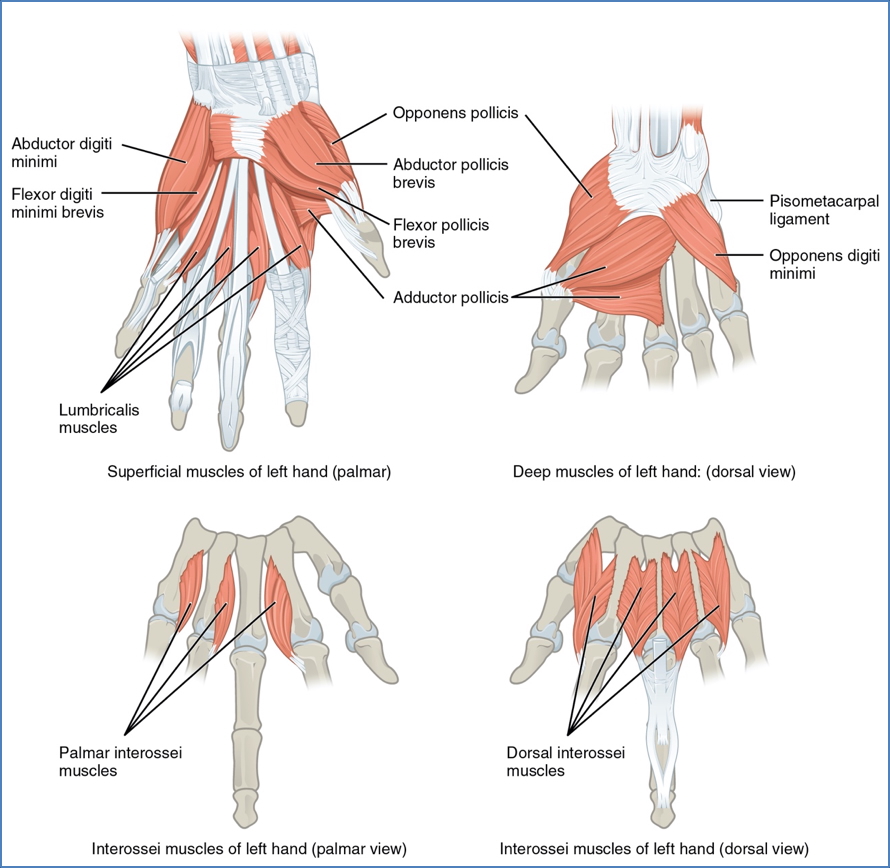
Intrinsic Hand Muscles
The intrinsic hand muscles are responsible for precision movements and fine motor control. These small muscles originate and insert within the hand, and are characterised by short tendons, small motor units, and high neuromuscular coordination.
Thenar Muscles (Thumb)
- Form the muscular “ball” at the base of the thumb.
- Primarily innervated by the median nerve, except adductor pollicis, which is supplied by the ulnar nerve.
- Adductor pollicis is not strictly part of the thenar group, but is often included due to its action on the thumb.
| Muscle | Origin → Insertion | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Abductor Pollicis Brevis | Flexor retinaculum → Lateral base of proximal phalanx of thumb | Abducts thumb at carpometacarpal joint |
| Flexor Pollicis Brevis | Flexor retinaculum & trapezium → Lateral base of proximal phalanx | Flexes thumb at CMC and MCP joints |
| Opponens Pollicis | Flexor retinaculum & trapezium → Anterior shaft of metacarpal 1 | Opposes thumb towards little finger |
| Adductor Pollicis | Capitate + bases of metacarpals 2–4 → Medial base of proximal phalanx | Adducts and opposes thumb |
Hypothenar Muscles (Little Finger)
- Located on the medial palm, forming the hypothenar eminence.
- All are innervated by the ulnar nerve.
| Muscle | Origin → Insertion | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Abductor Digiti Minimi | Pisiform → Medial proximal phalanx of digit 5 | Abducts little finger |
| Flexor Digiti Minimi Brevis | Hamate & flexor retinaculum → Medial proximal phalanx of digit 5 | Flexes little finger |
| Opponens Digiti Minimi | Hamate & flexor retinaculum → Medial shaft of metacarpal 5 | Opposes little finger |
Lumbricals
- 4 slender muscles within the palm, each associated with digits 2–5.
- Median nerve innervates the lateral 2; ulnar nerve innervates the medial 2.
| Muscle | Origin → Insertion | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Lumbricals 1–4 | From tendons of flexor digitorum profundus → Extensor expansions of digits 2–5 | Flex MCP joints and extend IP joints |
Interossei Muscles
Palmar Interossei (PAD – Palmar ADduct)
- 3 muscles (absent on metacarpal 3)
- Innervated by the ulnar nerve
| Muscle | Origin → Insertion | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Palmar Interossei (Index, Ring, Little) | Shaft of metacarpals 2, 4, 5 → Extensor expansions on same side | Adduct fingers, flex MCP joints, extend IP joints |
Dorsal Interossei (DAB – Dorsal ABduct)
- 4 bipennate muscles
- Deepest layer of palm, visible dorsally
- Innervated by the ulnar nerve
| Muscle | Origin → Insertion | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Dorsal Interossei (1–4) | Adjacent sides of two metacarpals → Extensor expansions of digits 2–4 | Abduct fingers, flex MCP joints, extend IP joints |
Extrinsic Muscles of the Hand
The extrinsic hand muscles originate in the forearm and insert into the hand via long tendons, enabling powerful movements. These muscles are responsible for flexion and extension of the wrist and fingers, and are divided into anterior flexors and posterior extensors.
Anterior Flexors (pass through carpal tunnel)
- Control finger and thumb flexion
- Large motor units for gross grip strength
- Flexor Digitorum Superficialis
- Flexor Digitorum Profundus
- Flexor Pollicis Longus
Posterior Extensors
- Located on the posterior forearm
- Responsible for finger extension and thumb movement
- Extensor Digitorum
- Extensor Digiti Minimi
- Extensor Indicis
- Extensor Pollicis Longus
- Extensor Pollicis Brevis
- Abductor Pollicis Longus
Summary – Upper Limb Muscles
Upper limb muscles can be grouped by region and function, including movements at the pectoral girdle, shoulder, elbow, wrist, and fingers. This includes intrinsic hand muscles for fine motor control and extrinsic muscles for powerful movements. For a broader context, see our Musculoskeletal Overview page.