Table of Contents
Overview – Ischaemic Heart Disease Drugs
Drugs used to treat Ischaemic heart disease (IHD) target three primary goals: improving coronary perfusion, reducing myocardial oxygen demand, and treating underlying atherosclerosis. Commonly used agents include organic nitrates, β-blockers, calcium channel blockers, and statins, among others. A strategic combination of these pharmacologic classes is essential for both symptomatic relief and long-term prevention of adverse cardiac events.
Treatment Goals in IHD
- Increase Coronary Blood Flow
- Organic Nitrates (e.g. GTN)
- Calcium Channel Blockers
- Potassium Channel Activators (e.g. Nicorandil)
- Reduce Myocardial Oxygen Demand
- ↓ Heart Rate → β-blockers
- ↓ Contractility → β-blockers, Ca²⁺ channel blockers
- ↓ Afterload & Preload → ACE inhibitors, vasodilators
- Treat Atherosclerosis & Prevent Thrombosis
- Statins (HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors)
- Ion Exchange Resins
- Ezetimibe (intestinal cholesterol absorption blocker)
- Prophylactic Anticoagulants: Heparin, Warfarin
Organic Nitrates
Classical Agents:
- Glyceryl Trinitrate (GTN) – dilates arteries and veins
- Isosorbide Mononitrate / Dinitrate – primarily venodilators
Mechanism:
- Act as exogenous nitric oxide (NO) donors.
- NO → stimulates guanylate cyclase in vascular smooth muscle → ↑ cGMP → ↓ intracellular Ca²⁺ → smooth muscle relaxation → vasodilation.
Therapeutic Effects:
- ↑ Coronary perfusion
- ↓ Preload (venodilation)
- ↓ Afterload (arteriodilation)
Clinical Use:
- Acute angina: sublingual tablets or sprays
- Prophylaxis: transdermal patches or slow-release tablets
Key Side Effects:
- Rapid tolerance → daily drug-free period required
- Hypotension

β-Blockers
Classical Agents:
- Propranolol, Atenolol, Esmolol, Pindolol
- Sotalol (also has Class III antiarrhythmic properties)
Mechanism:
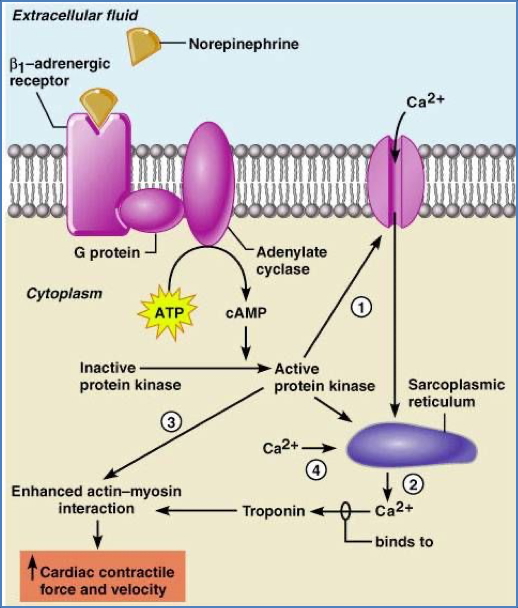
- Block β1-adrenergic receptors → ↓ sympathetic tone → ↓ HR and contractility → ↓ cardiac workload.
Cellular Actions:
- ↓ SA/AV node activity via reduced Na⁺/Ca²⁺ influx
- ↓ Myocyte contractility via ↓ intracellular Ca²⁺
Clinical Use:
- Tachyarrhythmias (e.g. atrial fibrillation)
- SVT
- Hypertension
- Angina (especially exertional)
Contraindications:
- Asthma (risk of bronchoconstriction)
- Concurrent calcium channel blockers → risk of fatal bradycardia
Key Side Effects:
- Sinus bradycardia
- Bronchospasm
- Rebound tachycardia if abruptly withdrawn
Calcium Channel Blockers
Classical Agents:
- Verapamil – heart-selective
- Nifedipine – vessel-selective
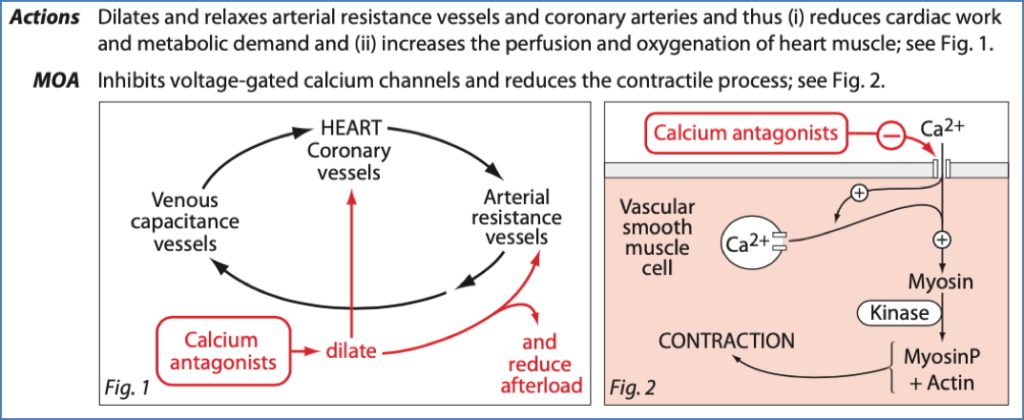
Mechanism:
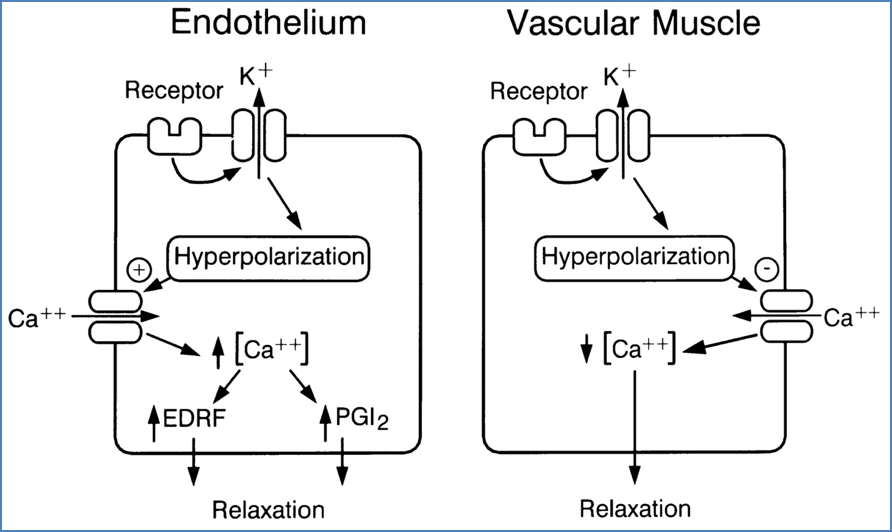
- Heart: Block VG-Ca²⁺ channels → ↓ SA/AV node conduction & myocyte contractility
- Vessels: Relax vascular smooth muscle → vasodilation
Clinical Use:
- SVT
- Variant angina (Prinzmetal’s)
- Hypertension (particularly nifedipine)
Contraindications:
- Co-use with β-blockers → risk of AV block and bradycardia
Key Side Effects:
- Heart block, bradycardia
- Hypotension, dizziness
Potassium Channel Activators
Agent:
- Nicorandil
Mechanism:
- Opens ATP-sensitive K⁺ channels in vascular smooth muscle → hyperpolarisation → vasodilation
- Also stimulates guanylate cyclase → ↑ cGMP → closes Ca²⁺ channels
Effects:
- ↓ Preload
- ↓ Afterload
- ↑ Coronary perfusion
Clinical Use:
- Angina
Key Side Effects:
- Headache (transient)
- Mucosal and gastrointestinal ulcers (unclear pathogenesis)
Drugs in Acute Myocardial Infarction (MI)
- Aspirin – antiplatelet
- Oxygen therapy
- Organic nitrates – vasodilation
- Anticoagulants – prevent clot progression
- β-Blockers – reduce oxygen demand
- ACE inhibitors – reduce afterload and prevent remodeling

Always refer to local MI management protocols before initiating therapy.
Summary – Ischaemic Heart Disease Drugs
Ischaemic heart disease drugs work by improving coronary perfusion, reducing myocardial oxygen demand, and managing the underlying atherosclerosis. Common treatments include organic nitrates for acute relief, β-blockers and calcium channel blockers to reduce cardiac workload, and statins and anticoagulants for long-term prevention. These pharmacological interventions are essential in both the acute and chronic management of IHD. For a broader context, see our Pharmacology & Toxicology Overview page.