Table of Contents
Overview – Cervicitis
Cervicitis is inflammation of the cervix, most commonly caused by sexually transmitted infections (STIs) such as Chlamydia trachomatis or Neisseria gonorrhoeae. It is a highly prevalent condition affecting up to 50% of women during their lifetime and can lead to symptoms like abnormal vaginal bleeding and discharge. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent complications, including pelvic inflammatory disease and increased risk of cervical neoplasia.
Definition
Cervicitis refers to inflammation of the cervix, typically due to infectious agents transmitted through sexual activity.
Aetiology
- Infectious Causes (Secondary to Vaginal Infections):
- Chlamydia trachomatis
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Trichomonas vaginalis
- Candida albicans
- Risk Factors:
- High levels of sexual activity
- Unprotected sex
- Multiple sexual partners
- History of STIs
Pathogenesis
- Ascending vaginal pathogens infect the cervical epithelium → inflammation and immune response
- Can be acute or chronic
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection can lead to persistent inflammation and premalignant changes
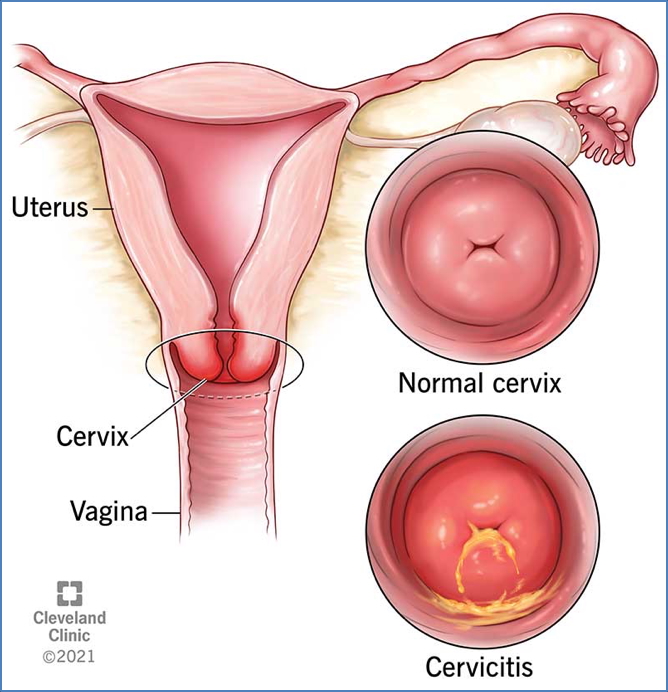
Morphology
Macroscopic
- Red, swollen, and inflamed cervix
- May have mucopurulent or mucoid discharge
Microscopic
- Cervical epithelial oedema
- Infiltration with inflammatory cells (mainly neutrophils)
- Possible cytopathic effects if HPV present
Clinical Features
- Prevalence: Affects ~50% of women at least once
- Symptoms:
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding:
- Post-coital
- Intermenstrual
- Postmenopausal
- Vaginal discharge (white, grey, or yellow ± odour)
- Dyspareunia (painful intercourse)
- Pelvic heaviness or pressure
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding:
Investigations
- Pelvic examination: Speculum visualisation of the cervix
- Pap smear: Detects cytological changes or inflammation
- Nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs) for:
- Chlamydia trachomatis
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Wet mount microscopy (if trichomoniasis suspected)
Management
- Empirical antibiotic therapy:
- Azithromycin 1g orally single dose
- OR Doxycycline 100mg orally twice daily for 7 days
- Partner notification and treatment (if STI identified)
- Avoid sexual contact until completion of treatment
Prognosis
- Good with appropriate treatment
- If HPV-related cervicitis persists → increased risk of progression to cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cancer
Summary – Cervicitis
Cervicitis is a common, often sexually transmitted, infection of the cervix that can present with abnormal vaginal bleeding and discharge. Early diagnosis and antibiotic treatment are essential to prevent complications. Chronic or HPV-related cervicitis carries a risk of cervical cancer. For more information, visit our Reproductive Health Overview page.